Published on November 6, 2020
There is a high chance you have been misled about the ‘identity’ of vitamin D!
 Vitamin D is, in fact, a nutrient.
Vitamin D is, in fact, a nutrient.
Too often we read articles that begin by saying “vitamin D is actually a hormone,” or that “few people view their vitamin D supplement as hormone replacement therapy,” or the opening of many scientific papers “vitamin D is a secosteroid hormone,” but this is simply misleading.
“Vitamin D” is a term that refers to several compounds. It is true that the form of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] or calcitriol, when made by the kidney and circulated in the blood, is a hormone. However, the majority of vitamin D in the circulation, 25-hydroxyvitmain D [25(OH)D or calcidiol], is not a hormone, nor is its precursor vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol. Therefore, the majority of “vitamin D” in the body is not a hormone, nor will it be converted to a hormone before being used, but it is a nutrient.
This is an important distinction, and supplementing with vitamin D is definitely NOT hormone replacement therapy. Beyond bone health, vitamin D as 25(OH)D is used by nearly every cell in the body as a signaling molecule. That means that most actions of vitamin D, its regulatory effects on immune cells for example, are not as a hormone but as a signaling molecule not under regulatory control. Today we will explain why most of the time vitamin D is actually a nutrient.
What is a Vitamin?
Vitamins are nutrients that we must get from outside the body, usually in our diet, because they cannot be made within the body, and are necessary for normal bodily functions and overall health. For this reason, vitamins are called essential nutrients. Vitamins are required in small quantities, and are distinct from other biologically important compounds such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids which are required in larger quantities. In general, vitamins play important roles in enzyme function and regulation, facilitating or controlling vital chemical reactions in the body’s cells. If a vitamin is not present in adequate levels in the body, a specific deficiency disease may develop.
“Vitamin D” meets this definition. As humans, our major source of vitamin D is the sun. UVB rays in sunshine convert a precursor in the skin to vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol. However, when we do not get enough sunlight or we are unable to make vitamin D because of the angle of the sun, we must get vitamin D from our diet and thus it becomes a vitamin. Cholecalciferol is found in a few dietary sources (such as fatty fish and fortified milk and margarine), or it can be taken as a supplement. Extreme vitamin D deficiency results in rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults.
What is a Hormone?
A hormone is a substance produced in one part of the body and released into the blood stream to carry out its regulatory functions on another part of the body and is itself under regulatory control. Hormones are important in maintaining balance or “homeostasis.” Hormones in very small quantities carry out their functions by producing a response from a specific organ or tissue.
“Vitamin D” in its role in maintaining normal calcium levels is also a hormone and levels of 1,25(OH)2D are regulated by parathyroid hormone which respond to calcium levels. Calcium levels must be kept in a very narrow range because of its importance in muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and blood clotting – these are functions that are vital to life. Calcium is also important for building bones, which also act as a calcium storage depot.
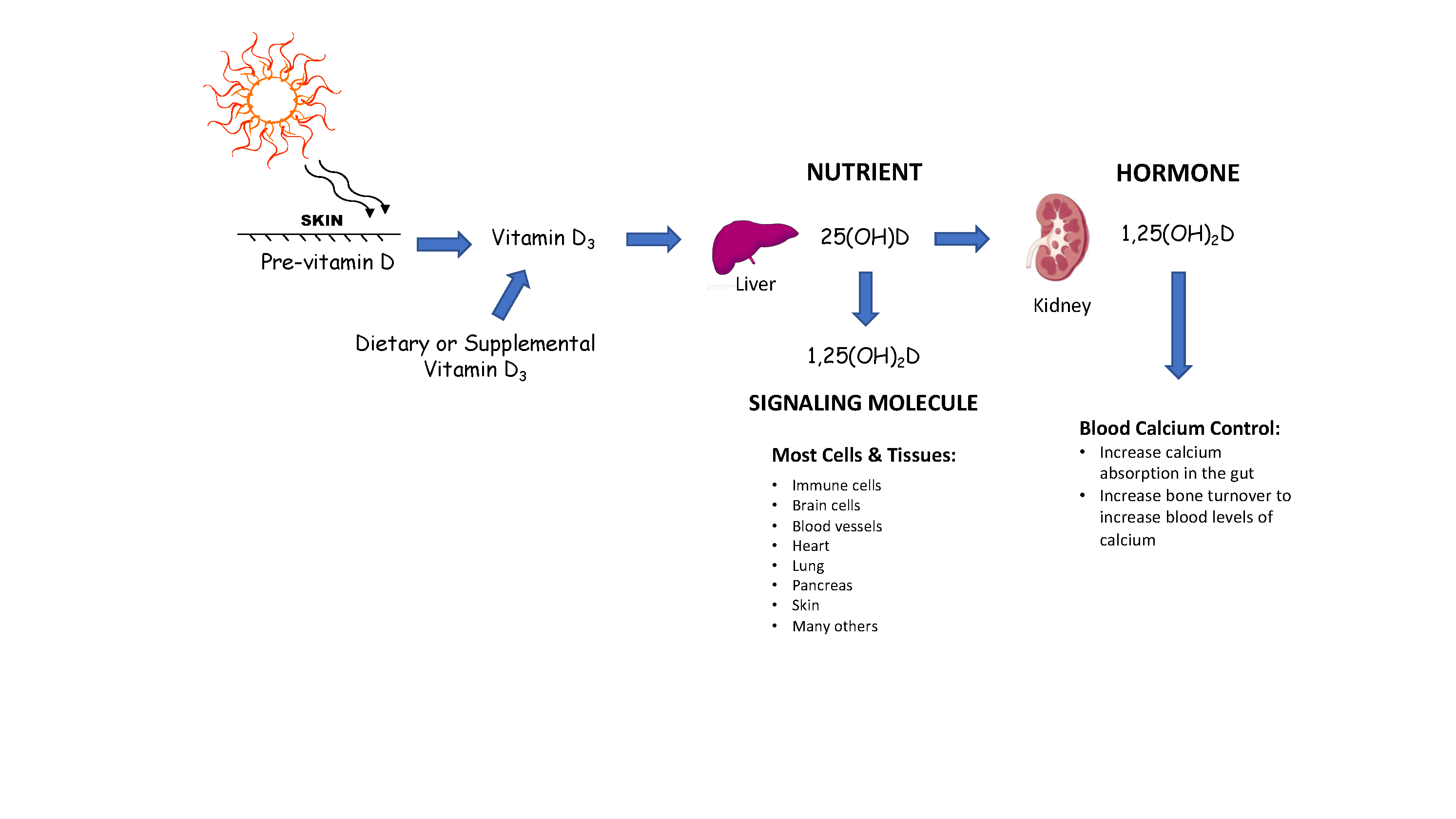
Vitamin D is Mostly a Nutrient
The diagram above demonstrates how vitamin D is handled in the body.
Whether from sun, food or supplement, the liver converts the majority of vitamin D3 to 25(OH)D. This is the form that we measure in the blood because it is present in the highest quantities and lasts for the longest period of time (for 2-3 months). The conversion of 25(OH)D to 1,25(OH)2D in the kidney produces the hormonal form of vitamin D that circulates in the blood.
Most other cells and tissues in the body have the enzyme needed to make 1,25(OH)2D and the receptor needed to use 1,25(OH)2D. However, this form of 1,25(OH)2D does not meet the requirements of a “hormone” because it is a signaling molecule that modulates the cell making it or nearby cells.
Circulating 25(OH)D may be thought of as a “pre-hormone,” but only in respect of the small amount that is converted in the kidneys to circulating 1,25(OH)2D, which then acts as a hormone. In the blood, 1,25(OH)2D has a concentration about 1/1000th that of circulating 25(OH)D (assuming a healthy level of 25(OH)D of 40-60 ng/ml) and is broken down very rapidly (within about 14 hours).
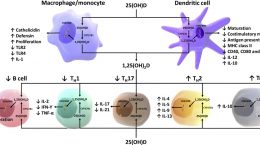
Research over the past several decades has shown that vitamin D is important to many biological pathways in the body. Of importance recently are the roles vitamin D plays in regulating immune cells. Other cells and tissues in which vitamin D plays regulatory roles include the brain, bone, heart, liver, lung, gut, muscles, skin, and teeth. In fact, low levels of vitamin D have been associated with many different diseases of these systems including autoimmune diseases, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, dementia and cognitive decline, respiratory infections and COVID-19, among others.
What is the take-home message? It is more accurate to refer to vitamin D as a nutrient, not a hormone!
REFERENCES:
Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000. Signaling Molecules and Their Receptors.
Vieth R. Vitamin D supplementation: cholecalciferol, calcifediol, and calcitriol. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2020; 74: 1493–1497.
Do you know YOUR vitamin D level? Could deficiency be hindering your overall health?
Could a vitamin D deficiency be putting a damper on your health and immune response? Do you know your levels of other immune-important nutrients as well?
Using the GrassrootsHealth Custom Kit Builder, you can create a test kit that measures your vitamin D level and other important nutrients (such as omega-3s and magnesium), as well as your CRP level. Click here to build and order your test kit today – measure your status and take the steps necessary to improve them if needed; make an impact on your health today and for your future! When you know what your levels are, you can determine next steps to take and how much supplementation may be needed if you are not at your target levels.
Concerned specifically about nutrients important to your immune response? Find out levels of these nutrients by testing your vitamin D, omega-3s, magnesium and other essential elements (including selenium), as well as your inflammation levels, with the new Immune Boost home test kit offered by GrassrootsHealth. Measuring levels is the only way to know if you are supporting your immune system and whether additional changes should be made, with supplementation, dietary changes, or both.
Enroll now with the Full Immune Boost Panel (which includes tests for vitamin D, Omega-3 Index, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, and hsCRP), and get 10% off when you use coupon code BoostTen at checkout.
What Does it Take YOU to Get Your D to 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L)?
Did you know your health could be greatly affected by making sure you have a vitamin D level of at least 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L)? Help us help you.
STEP 1 – Do you know what your vitamin D level is? If not, be sure to test today to find out.
STEP 2 – Determine your target level. Are you at your target level? Experts recommend a level of at least 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L).
STEP 3 – Need to boost your level? Use the D*calculator to see how much vitamin D it may take to reach your target. Opt for the Loading Dose for a quicker boost.
STEP 4 – Optimize how your body absorbs and utilizes vitamin D with co-nutrients and these simple steps.
STEP 5 – Re-Test! This is an important step to make sure you have reached your target level, and to ensure you are not taking too much! Re-testing after 3-4 months is recommended.
STEP 6 – Adjust, Repeat…
Give your immune system the nutrients it needs to support a healthy you and protect yourself from unnecessary diseases, especially COVID-19.
NEWS ALERT
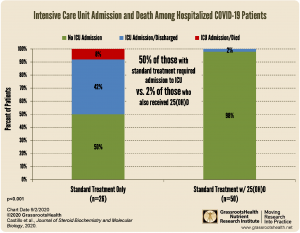 The first Randomized Controlled Trial on vitamin D and COVID-19 has shown a 96% lower risk of ICU admission for those receiving vitamin D (as 25(OH)D to quickly boost vitamin D blood levels) along with the standard treatment, compared to those receiving standard treatment alone.
The first Randomized Controlled Trial on vitamin D and COVID-19 has shown a 96% lower risk of ICU admission for those receiving vitamin D (as 25(OH)D to quickly boost vitamin D blood levels) along with the standard treatment, compared to those receiving standard treatment alone.
These results support many previous observational studies showing a relationship between vitamin D levels and intake and COVID-19 severity.
Review the Latest Nutrient Research for COVID-19
GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute has launched the new Immune Boost project with the use of our myData-myAnswers nutrient health system that nearly 15,000 people are already using for their health. Specific markers that influence immune health are suggested for testing as part of this project including:
- Vitamin D
- Omega-3 Index
- Essential elements magnesium, selenium, and zinc
- hsCRP
Our goal is to demonstrate how one can use the Nutrient Research Model established by Dr. Robert Heaney to show the effect of vitamin D serum levels of at least 40 ng/ml (100 nmol/L) on risk reduction for all ethnicities in the population. Status and intake of other nutrients will also be analyzed for any type of relationship to immune status and symptom severity. Join the project today!
Please let us know if you’re interested in helping sponsor this project.
CLICK HERE for updates and new information about the project.
Through GrassrootsHealth Nutrient Research Institute, you can also test your essential elements magnesium, copper, zinc and selenium, toxins such as lead, mercury and cadmium, as well as your omega-3 levels, inflammation levels and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level. Find out your levels today! Log on to the test selection page (click the link below) to get your tests and see for yourself if your levels can be improved.
Make sure you track your results before and after, about every 6 months!
Click Here to Access the Test Page
How can I track my nutrient intake and levels over time?
To help you track your supplement use and nutrient levels, GrassrootsHealth has created the Personal Health Nutrient Decision System called
For each specific supplement, you can track what days you take it, how much, and many other details. This will help you know your true supplemental intake and what patterns of use work for you to reach and maintain optimum nutrient levels. Check it out today!