Published on April 22, 2024
Another meta-analysis confirms previous findings on risk reductions in cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death provided by omega-3 fatty acids
Key Points
- There have been many studies on the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health and the prevention of ischemic events; omega-3s have also been shown to inhibit the development and progression of atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease involving the immune cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and vascular endothelial cells
- Another 2023 meta-analysis supports findings from other previous studies on omega-3s and cardiovascular disease, showing that omega-3 supplementation, especially with higher levels of EPA and DHA, reduced CVD and CV mortality
- Getting too many omega-6 fatty acids (specifically LA, which is over-abundant in today’s Western diet) can affect the efficacy and use of omega-3s within the body’s tissues, one reason measuring levels of both omega-3s and omega-6s is important for cardiovascular and overall health
Get 15% Off Test Kits Measuring Your Omega-3s with Code OMEGA3S
 There have been many studies on the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health and the prevention of ischemic events. One meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials that used supplementation of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA found a preventive effect of supplementation on cardiovascular disease (CVD), with a stronger effect associated with higher doses especially for CVD events and heart attack. Another study found a significantly lower risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease mortality, and death from heart attack among habitual fish oil users. The VITAL trial, which focused on cancer and cardiovascular health, found several significant benefits among those assigned to omega-3s (1000 mg/day) vs. placebo, including a 28% reduced risk of heart attack overall, with a 77% reduced risk of heart attack among African Americans and a 94% reduced risk of heart attack among African Americans with diabetes, and a post-hoc analysis showing a 50% reduced risk of death from heart attack.
There have been many studies on the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids for cardiovascular health and the prevention of ischemic events. One meta-analysis of 40 randomized controlled trials that used supplementation of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA found a preventive effect of supplementation on cardiovascular disease (CVD), with a stronger effect associated with higher doses especially for CVD events and heart attack. Another study found a significantly lower risk for all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease mortality, and death from heart attack among habitual fish oil users. The VITAL trial, which focused on cancer and cardiovascular health, found several significant benefits among those assigned to omega-3s (1000 mg/day) vs. placebo, including a 28% reduced risk of heart attack overall, with a 77% reduced risk of heart attack among African Americans and a 94% reduced risk of heart attack among African Americans with diabetes, and a post-hoc analysis showing a 50% reduced risk of death from heart attack.
Omega-3s have also been shown to inhibit the development and progression of atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammatory disease involving the immune cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, and vascular endothelial cells.
Another Meta-analysis Confirms Findings on Omega-3s and Heart Health
A 2023 meta-analysis by Bae et al. looked at data from 17 large randomized controlled trials (RCTs), each including 500 participants or more and a follow-up time of a year or greater; the total number of participants in the analysis was 143,410. The authors looked to address the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on cardiometabolism while also assessing the clinical and biological effects of omega-3s on health.
This study, as with many other previous studies on omega-3s and CVD, found that omega-3 supplementation, especially with higher levels of EPA and DHA, reduced CVD and CV mortality. More specifically, omega-3 supplementation was related to a significantly reduced risk of cardiovascular death (6%) and fatal or nonfatal heart attack (17%). Greater effects were seen on major adverse cardiovascular events, cardiovascular death, and fatal or nonfatal heart attacks when supplementing with EPA alone vs EPA with or without DHA.
No significant effects were found for stroke or all-cause mortality among those supplementing with omega-3s. There was no significantly increased risk of bleeding found overall, however, there was a dose-related increased risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation with omega-3 supplementation.
How Omega-3s Mitigate Atherosclerosis and Reduce CVD Risk
There are many beneficial health effects provided by omega-3 fatty acids that can contribute to a reduced risk of atherosclerosis and CVD, including
- reduced triglyceride concentrations
- anti-inflammatory effects
- immunomodulatory effects
- antiplatelet effects
- vascular protective effects
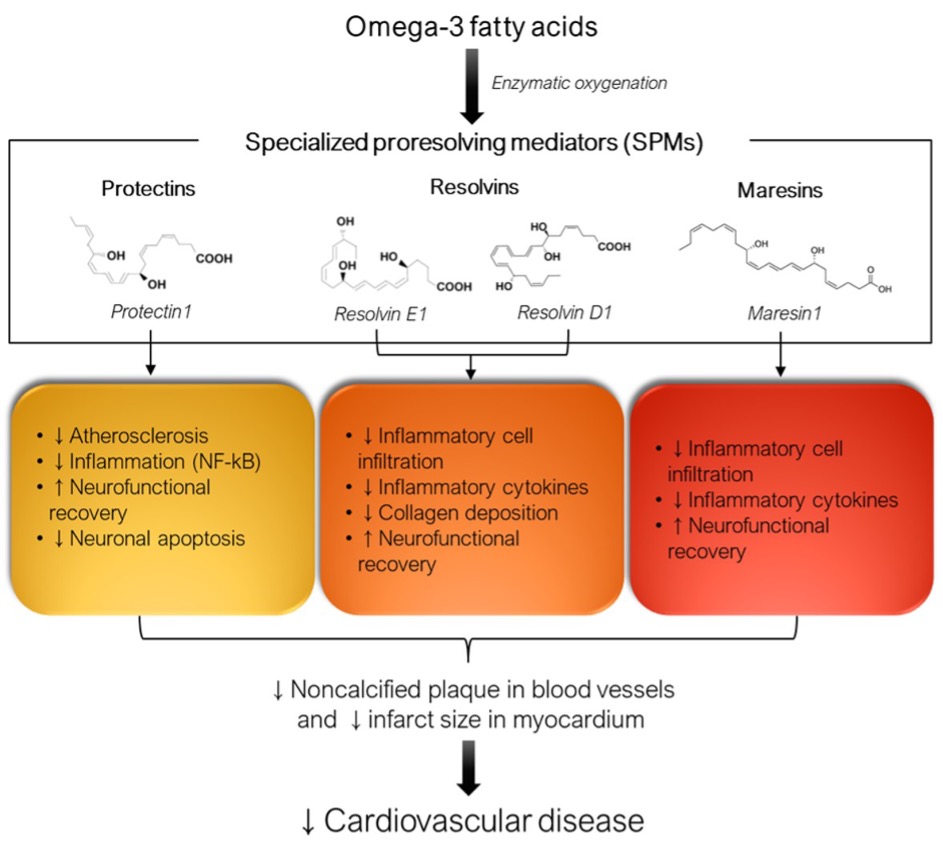
Another possible additional effect noted by the study includes its role in restoring glucose homeostasis via the gut microbiota. Each of these actions along with other potential mechanisms of omega-3 fatty acids on the reduction of CVD are included in the illustration below.
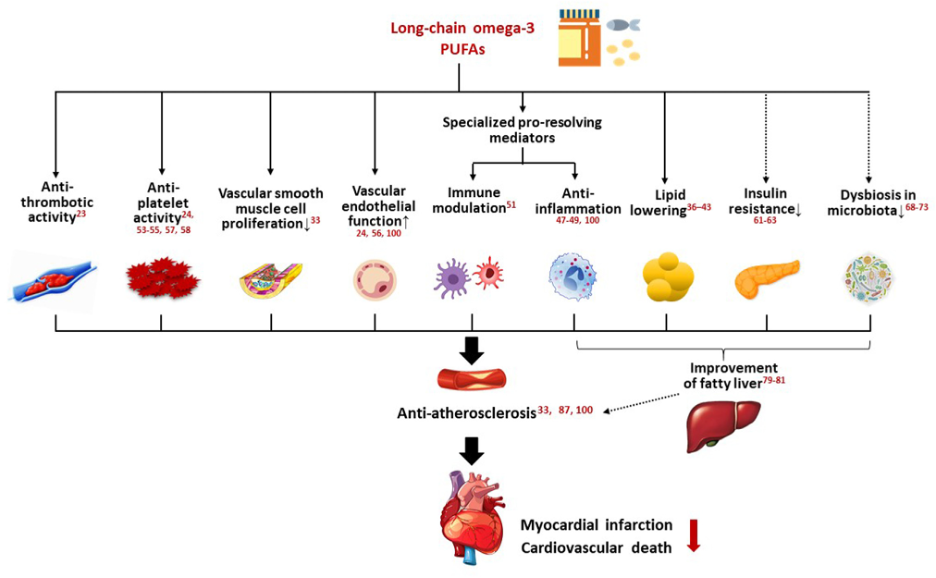
The following diagram also illustrates how omega-3 fatty acids can benefit cardiovascular health and contribute to the resolution of inflammation through specialized pro-resolving mediators, or SMPs.
Getting Too Many Omega-6s Can Interfere with the Actions of Omega-3s
We have previously discussed how excess omega-6 intake can contribute to chronic inflammation or an Omega-3 Index that does not increase as expected, and how the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) into arachidonic acid (AA), both omega-6 fatty acids, is increased when insulin levels are elevated – a reason maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is also important to controlling inflammation.
Getting too many omega-6 fatty acids (specifically LA, which is over-abundant in today’s Western diet) can also affect the efficacy and use of omega-3 fatty acids within the body’s tissues. This is because the conversion of both LA into AA (omega-6s) and ALA into EPA (omega-3s) utilize the same enzyme, hence creating a competitive relationship between the two. The authors put it clearly,
“…the higher the ratio of LA (an omega-6) to ALA (an omega-3), the more inhibited the synthesis of EPA and DHA from ALA.”
It is for this reason that measuring the AA:EPA Ratio and Omega-6:Omega-3 Ratio can be beneficial for providing insight on how to address levels overall for cardiovascular health and other health outcomes affected by omega-3s.
An important note is that, while ALA is the most common omega-3 fatty acid and can be converted into EPA and then into DHA, the conversion rate is low (less than 15%), making direct intake of EPA and DHA through supplements and diet essential for healthy levels.
Get 15% Off Test Kits Measuring Your Omega-3s with Code OMEGA3S
How Much EPA and DHA Do You Need?
 Whether deciding to get more EPA or DHA for your particular health benefits, it is still important to make sure the combined intake is helping to achieve and maintain an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%. An analysis of GrassrootsHealth data found that approximately 1,300 mg/day of EPA+DHA was needed for 50% of the population and 1,900 mg/day was needed for 90% of the population to achieve and Omega-3 Index of 8%. It is important to point out that, similar to the large variability seen with vitamin D dose response to intake, these intake amounts are averages and there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount. For example, our initial analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, we recommend that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose.
Whether deciding to get more EPA or DHA for your particular health benefits, it is still important to make sure the combined intake is helping to achieve and maintain an Omega-3 Index of at least 8%. An analysis of GrassrootsHealth data found that approximately 1,300 mg/day of EPA+DHA was needed for 50% of the population and 1,900 mg/day was needed for 90% of the population to achieve and Omega-3 Index of 8%. It is important to point out that, similar to the large variability seen with vitamin D dose response to intake, these intake amounts are averages and there is a large amount of variability in the omega-3 status for different people with the same intake amount. For example, our initial analysis showed that the range of response with 1000 mg of EPA+DHA per day was 5.7% to 10.2%. Therefore, we recommend that individuals measure their Omega-3 Index and determine a personalized dose.
Once results are received, consider your next steps for adjusting the Omega-3 Index, such as how to choose between the different types of omega-3 sources, how to evaluate and choose an omega-3 supplement, and how to achieve a desired Omega-3 Index using an estimated dose of EPA and DHA as determined by our Omega-3 calculator. Taking simple dietary steps to increase consumption of foods rich in EPA and DHA can also help increase your Omega-3 Index.
What Are Your Levels?
As part of the GrassrootsHealth D*action project, you can measure your:
- Vitamin D
- Magnesium PLUS Essential and Toxic Elements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- hsCRP
- HbA1c
- TSH
- Type 1 Diabetes Autoantibodies
Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.
Enroll and test your levels today, learn what steps to take to improve your status of vitamin D (see below) and other nutrients and blood markers, and take action! By enrolling in the GrassrootsHealth projects, you are not only contributing valuable information to everyone, you are also gaining knowledge about how you could improve your own health through measuring and tracking your nutrient status, and educating yourself on how to improve it.