Published on August 29, 2023
New discoveries from last week’s study prompts comments from GrassrootsHealth’s Principal Investigator, Cedric Garland Dr.PH, with excitement for more vitamin D confirmations in the near future
Key Points
- A new study by Kanno et al. found that vitamin D supplementation improved the chances of survival by more than 2.5 fold among individuals with digestive cancers who were p53-immunoreactive, compared to those not taking vitamin D – a finding that “now proves beyond a doubt the power of vitamin D against cancer recurrence and fatality at the clinical level”
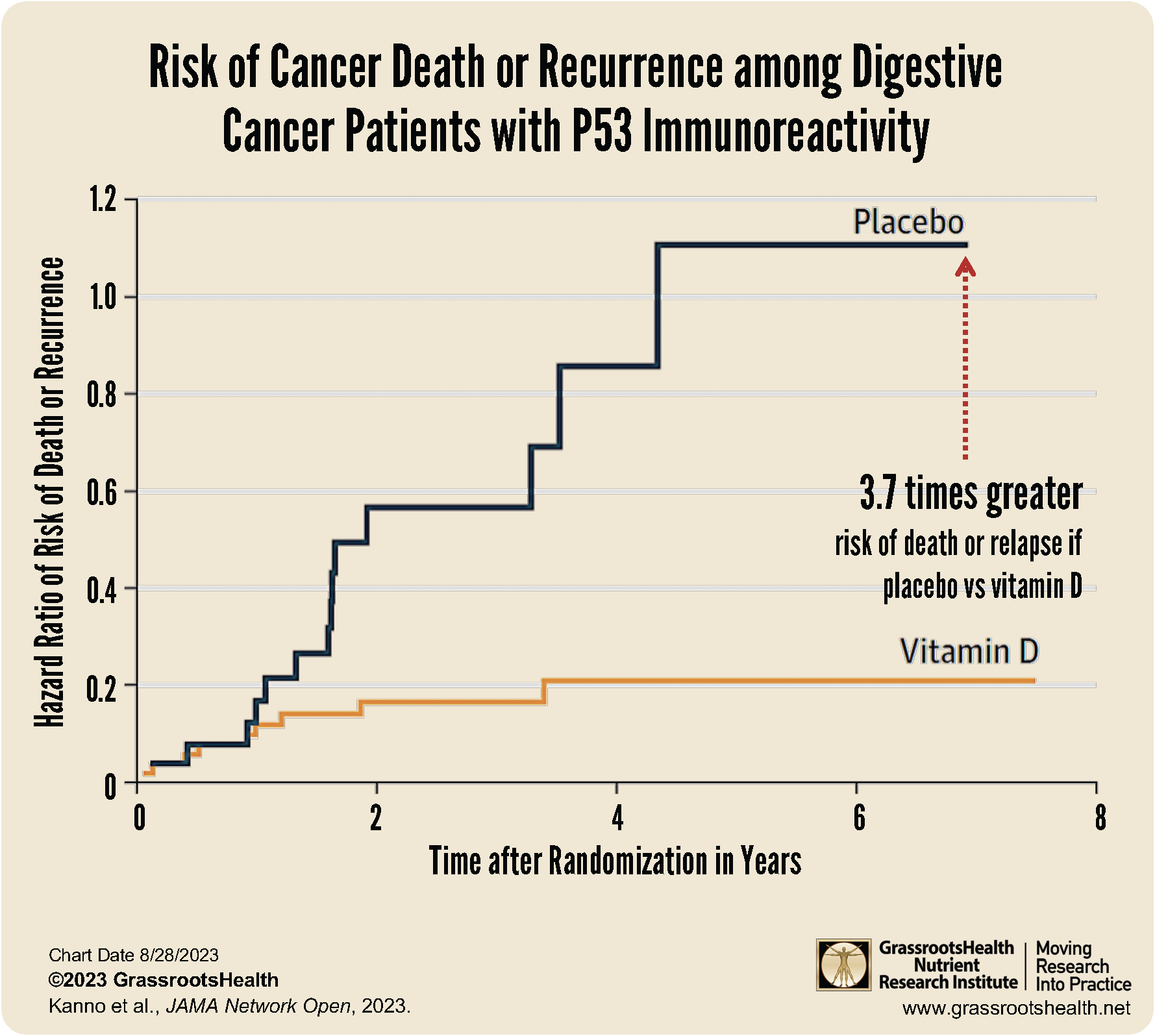
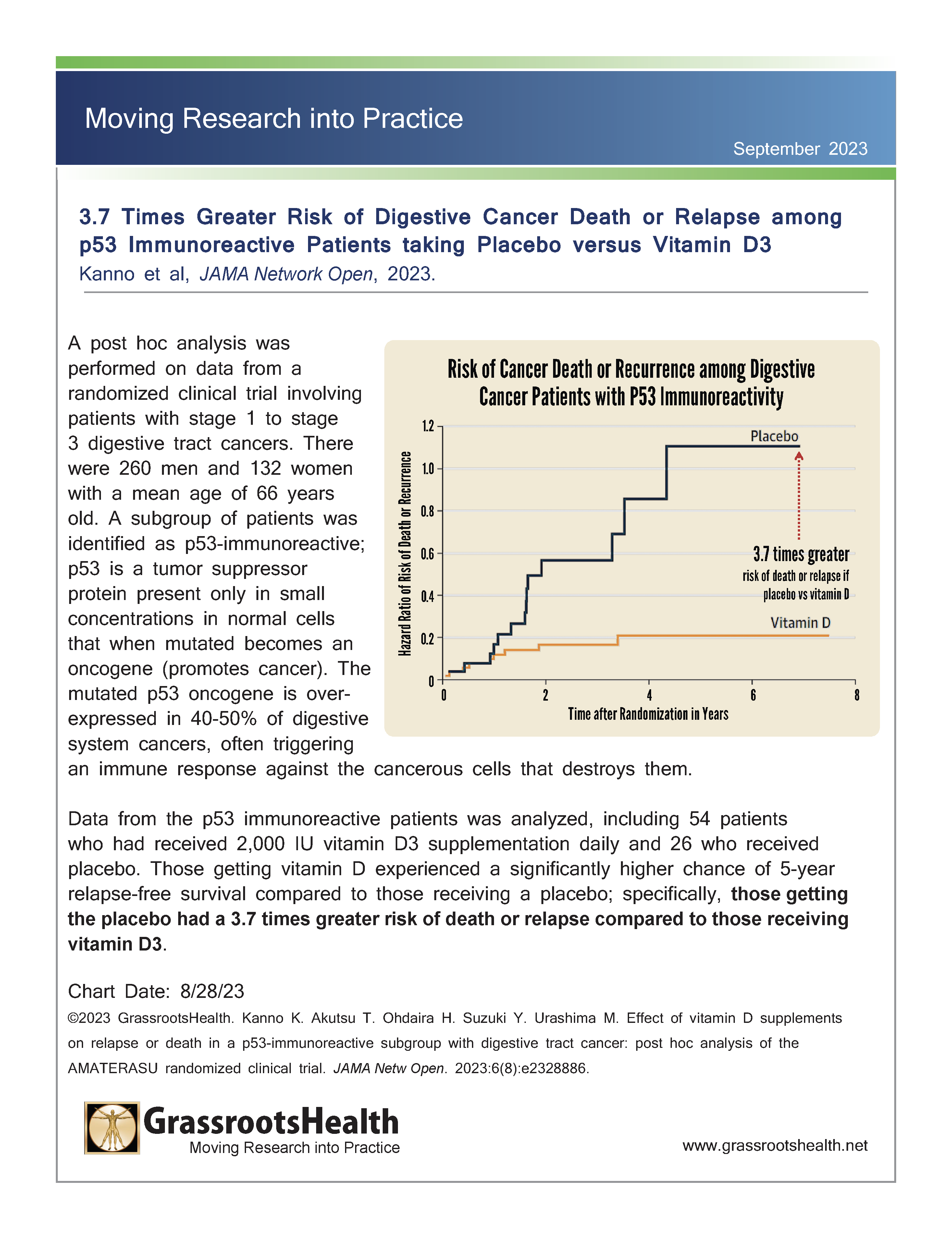
- An analysis of all patients with any evidence of p53 overexpression found a 3.7 times greater risk of death or relapse in the placebo group than in the group that received 2000 IU/day of vitamin D3
- According to Dr. Garland, the 2000 IU/day D3 dose used by Kanno et al. probably is not a large enough dose to assess the potential benefits of a more appropriate 4000 or 5000 IU/day vitamin D3 intake or a high level of vitamin D photosynthesis in the skin on a daily basis that raises the 25(OH)D to a more ideal concentration of about 60 ng/ml (150 nmol/L); a study should be performed now that uses an achieved serum concentration of 60 ng/ml as the treated group, compared with a placebo group having 25(OH)D concentration of less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L)
 On Tuesday of last week, a new study was published in the JAMA Open Network titled “Effect of Vitamin D Supplements on Relapse or Death in a p53-immunoreactive Subgroup with Digestive Tract Cancer: Post Hoc Analysis of the AMATERASU 5 Randomized Clinical Trial” – its key finding was that vitamin D supplementation improved the chances of survival by more than 2.5 fold among individuals with digestive cancers who were p53-immunoreactive, compared to those not taking vitamin D.
On Tuesday of last week, a new study was published in the JAMA Open Network titled “Effect of Vitamin D Supplements on Relapse or Death in a p53-immunoreactive Subgroup with Digestive Tract Cancer: Post Hoc Analysis of the AMATERASU 5 Randomized Clinical Trial” – its key finding was that vitamin D supplementation improved the chances of survival by more than 2.5 fold among individuals with digestive cancers who were p53-immunoreactive, compared to those not taking vitamin D.
Dr. Cedric Garland, Principal Investigator of GrassrootsHealth’s vitamin D*action study, is one of the world’s leading senior researchers and experts on vitamin D and cancer. He published his first paper on the connection between sunlight and vitamin D with colon cancer back in 1980 (re-published in 2006) – and hasn’t stopped researching it since. His research has shown a clear and significant lower risk of colorectal cancer and other cancers with higher serum 25(OH)D concentrations.
Read below for comments from Dr. Garland on this latest vitamin D discovery.
“I think this may convince some of the last skeptics who’ve been needlessly skeptical of the power of vitamin D to arrest cancer in its tracks.” Dr. Cedric Garland
A great message just came in from Dr. Michael Holick. He believes this study released by JAMA Open Network of a few digestive cancers, including colorectal cancer, by Kanno et al. of Japan, now proves beyond a doubt the power of vitamin D against cancer recurrence and fatality at the clinical level. This study will finally eliminate the remaining people who doubted that vitamin D saves lives from cancer. He has written about this in a commentary in JAMA Open, and this is summarized in a Media Release from JAMA Open.
The paper asserts that 2000 IU/day of vitamin D3 increases the immune response to mutated p53 protein that is present in roughly half of colorectal cancer patients. The authors note that the unmutated p53 gene product found in normal tissue cells is a known tumor suppressor protein and is generally present only in rather small concentrations in normal cells. Once the DNA that codes for it has been mutated (a missense point mutation) it goes wild in the cell and rises to a very high intracellular concentration. (You’ll recall that a missense mutation is a point mutation where a mutation to a single nucleotide creates a codon that codes for a different amino acid than the wild form, also known as a SNP).
When the concentration of this nasty mutated p53 protein rises to very high concentration in a cell, they assert that it’s then overexpressed on the outer surface of the cell membrane. They theorize that a high level of mutant p53 on the cell membrane stirs up the immune system, causing it to attack the cell. Paraphrasing them, they seem to say that attack by the immune system on cells whose membranes are covered with mutant p53 protein is a natural form of “immunotherapy” against some types of cancer.
About 40-50% of these cancers have evidence from the pathological tissue, obtained using a dye marker, or from an abnormally high level in the serum of an antibody to p53 protein. These mutant p53-overburdened cancers are susceptible to vitamin D therapy, boosting the normal human immune response using 2000 IU/day of vitamin D3. This could save lives of colorectal cancer patients and other cancer patients who have mutant p53 genes in the tumor. This is shown most clearly by the survival curves for vitamin D and placebo groups in the Visual Abstract that comes with the PDF of the paper, including figure 4a below, showing a 3.7 times greater risk of death or relapse in the placebo group than in the group that received 2000 IU/day of vitamin D3, among all patients with any evidence of p53 overexpression.
This finding is based on just a few cases, but I think it is still profound. It’s the kind of study where you might need Fisher’s exact test (a statistical significance test used when sample sizes are small). But, given the epidemiological context that we have provided over many years, along with replications by William Grant, PhD, it is quite logical. Now we need the same type of study performed for breast cancer and leukemia.
In the meantime, this is full of promise for stopping cancer spread, recurrence and risk of fatality. I think this may convince some of the last skeptics who’ve been needlessly skeptical of the power of vitamin D to arrest cancer in its tracks. It’s a cause for celebration despite the small sample!
As always,
Cedric
When Asked “What could be done next?”
The 2000 IU/day D3 dose used by Kanno et al. probably is not a large enough dose to assess the potential benefits of a more appropriate 4000 or 5000 IU/day vitamin D3 intake or a high level of vitamin D photosynthesis in the skin on a daily basis that raises the 25(OH)D to a more ideal concentration of about 60 ng/ml (150 nmol/L). (25(OH)D may be a more likely marker of the serum native vitamin D3 concentration than the active agent, which the epidemiology suggests is the main actor in cancer chemoprevention).
A study should be performed now that uses an achieved serum concentration of 60 ng/ml as the treated group, compared with a placebo group having 25(OH)D concentration of less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L).
Such a post-hoc analysis also should be done of the VITAL clinical trial population and should measure the p53 antibody in stored serum, which may still be available at Harvard. A nested case-control could confirm the very promising Kanno et al. results. It would not be expensive to perform. We should also start a similar nested case-control study of breast cancer survival in premenopausal and postmenopausal women in the VITAL population or other cohorts. This could include The Johns Hopkins Operation Clue cohort, if any serum from cancer patients has been saved.
In the meantime, every patient in North America and Europe with colorectal cancer should be tested for p53 antibodies in their serum, and all cancer tissues obtained from this anatomical region should be tested for overexpression of the mutated p53 protein if resources allow. The same should be done for samples of patients with premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer.
Measure Your Vitamin D Level through D*action Today!
Create Your Custom Home Test Kit
 Measure your vitamin D levels at home as part of the D*action project! To know if you are getting enough, make sure you test today!
Measure your vitamin D levels at home as part of the D*action project! To know if you are getting enough, make sure you test today!
You can also measure your:
- Vitamin D
- Magnesium PLUS Essential and Toxic Elements
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- hsCRP
- HbA1c
- TSH
- Type 1 Diabetes Autoantibodies
Did you know that each of the above can be measured at home using a simple blood spot test? As part of our ongoing research project, you can order your home blood spot test kit to get your levels, followed by education and steps to take to help you reach your optimal target levels. Start by enrolling and ordering your kit to measure each of the above important markers, and make sure you are getting enough of each to support better mood and wellbeing!
Create your custom home test kit today. Take steps to improve the status of each of these measurements to benefit your overall health. With measurement you can then determine how much is needed and steps to achieve your goals. You can also track your own intakes, symptoms and results to see what works best for YOU.